Complete Guide to Light Bulb Base Types: Understand E, B, G/GU Bases at a Glance
Whether you’re replacing a burnt-out bulb at home or selecting lighting fixtures for a new project, the very first question you must answer is simple yet essential: does the bulb base match the socket?
Choosing the right bulb is much easier than it looks. Once you understand the basic categories of bulb bases, everything becomes straightforward. This guide walks you through the three most common base types—Edison screw (E series), bayonet (B series), and pin-style (G/GU series)—so you can instantly recognize any standard bulb base.

The Three Most Common Light Bulb Base Categories
Although the lighting market includes many base variations, the vast majority fall into just three major families: E-series Edison screw bases, B-series bayonet bases, and G/GU-series pin bases. Each follows a clear naming convention, making it easy to identify the correct replacement.
1. E-Series: Edison Screw Bases

If you only remember one type of bulb base, it will likely be the E series. Invented by Thomas Edison, this screw-in style is the most widely used base type in modern lighting. The naming is intuitive: the letter “E” stands for Edison, and the number indicates the base diameter in millimeters.
Common E-Series Specifications and Applications
| Type | Diameter | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|
| E14 | 14 mm | Decorative lamps, chandeliers, small desk lamps, refrigerator bulbs |
| E27 | 27 mm | Main household lighting, ceiling fixtures, floor lamps |
| E40 | 40 mm | Industrial lighting, street lights, high-power fixtures |
Quick tip: Match the numbers—same diameter means compatibility.
2. B-Series: Bayonet Bases
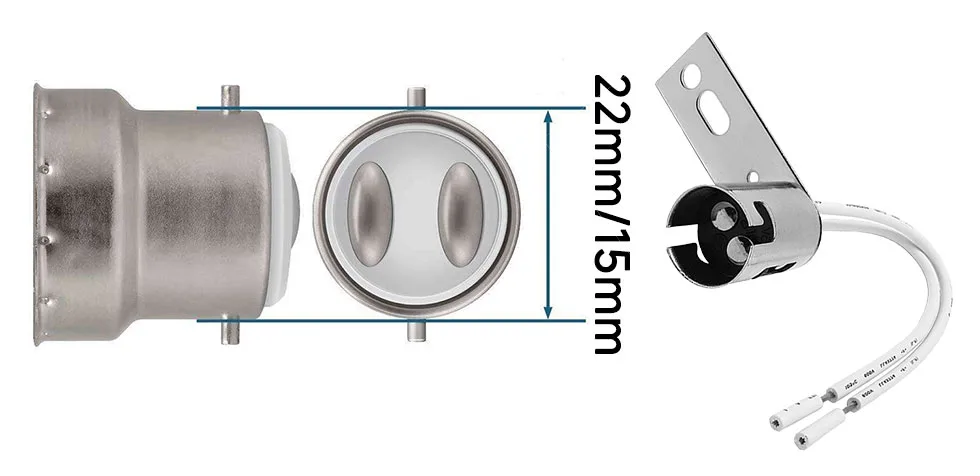
Bayonet bases use a “push and twist” mechanism instead of a screw thread. They are less common in some regions, but they remain a mainstream standard in the United Kingdom, Australia, New Zealand, and several other countries. The naming system is straightforward: “B” stands for bayonet, and the number refers to the base diameter.
Common B-Series Types
- B22d (22 mm): Widely used in many Commonwealth countries; similar use cases to E27.
- B15d (15 mm): Typical in compact, specialty, or marine lighting applications.
3. G / GU Series: Pin Bases
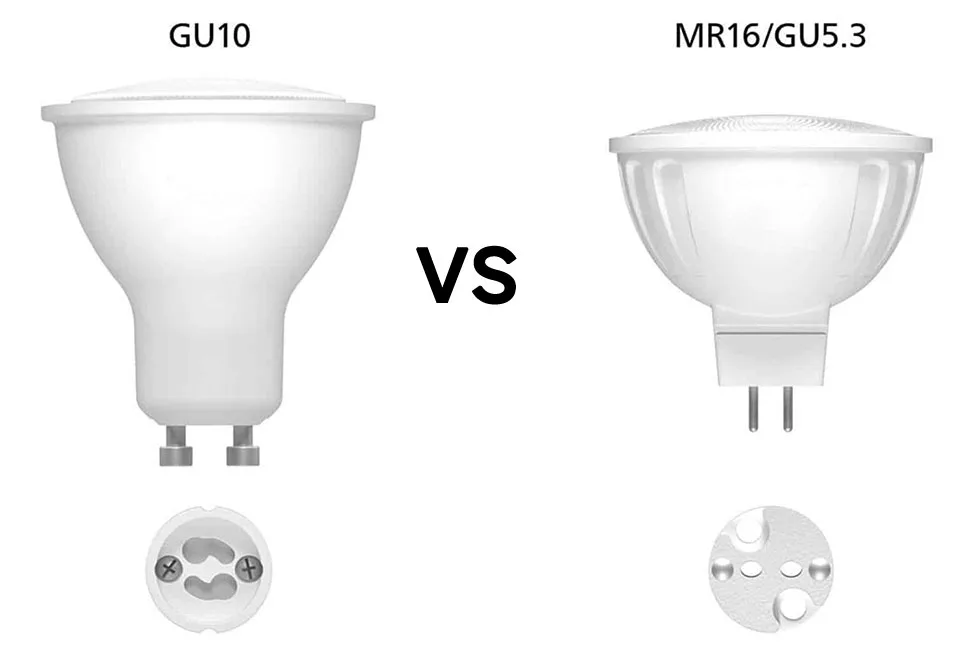

Pin-type bases are common in spotlights, downlights, and tubular lamps. The naming logic is easy to understand: “G” often refers to glass (historically) or pin-type construction, and the number indicates the distance (in mm) between the center points of the pins. When the code includes a “U,” it means the base has a special locking or alignment feature—GU10 being the most common example.
Popular Pin-Base Types
| Type | Pin Spacing | Applications |
|---|---|---|
| GU10 | 10 mm | Spotlights and track lights (insert and twist to lock) |
| G9 | 9 mm | Decorative wall lights and compact interior fixtures |
| G53 | 53 mm | Commercial display lighting (AR111/MR16 large format) |
| G13 | 13 mm | Fluorescent tubes such as T8 or T12 |
Check This Before Installing: Voltage Matters
Even if the base fits perfectly, that doesn’t guarantee safe operation. The bulb voltage must match your local power supply (such as 110V or 220V). Using the wrong voltage can cause flickering, failure, or even safety hazards. Always inspect the voltage information printed on the bulb’s packaging before purchasing.
Final Thoughts: Bulb Bases Are Simpler Than They Look
Once you understand the three major base families—E, B, and G/GU—and what the numbers represent, identifying bulb interfaces becomes effortless. The next time a light goes out, simply compare the socket with the reference tables and images in this guide, and you’ll know exactly which replacement to choose.
If you’d like to learn more about lighting, LED technology, or fixture selection, feel free to explore our knowledge base for more practical guides and tips.